Simple Gastric Anastomosis Bypass (OAGB): A Comprehensive Overview
The Simple Gastric Anastomosis Bypass, commonly referred to as One-Anastomosis Gastric Bypass (OAGB) or Mini Gastric Bypass (MGB), is a bariatric surgical procedure developed as a simpler alternative to the traditional Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass (RYGB). Since its introduction in the late 1990s, OAGB has gained popularity for its effectiveness in treating obesity and obesity-related health conditions, coupled with its technical simplicity and shorter operative time.
What Is OAGB?
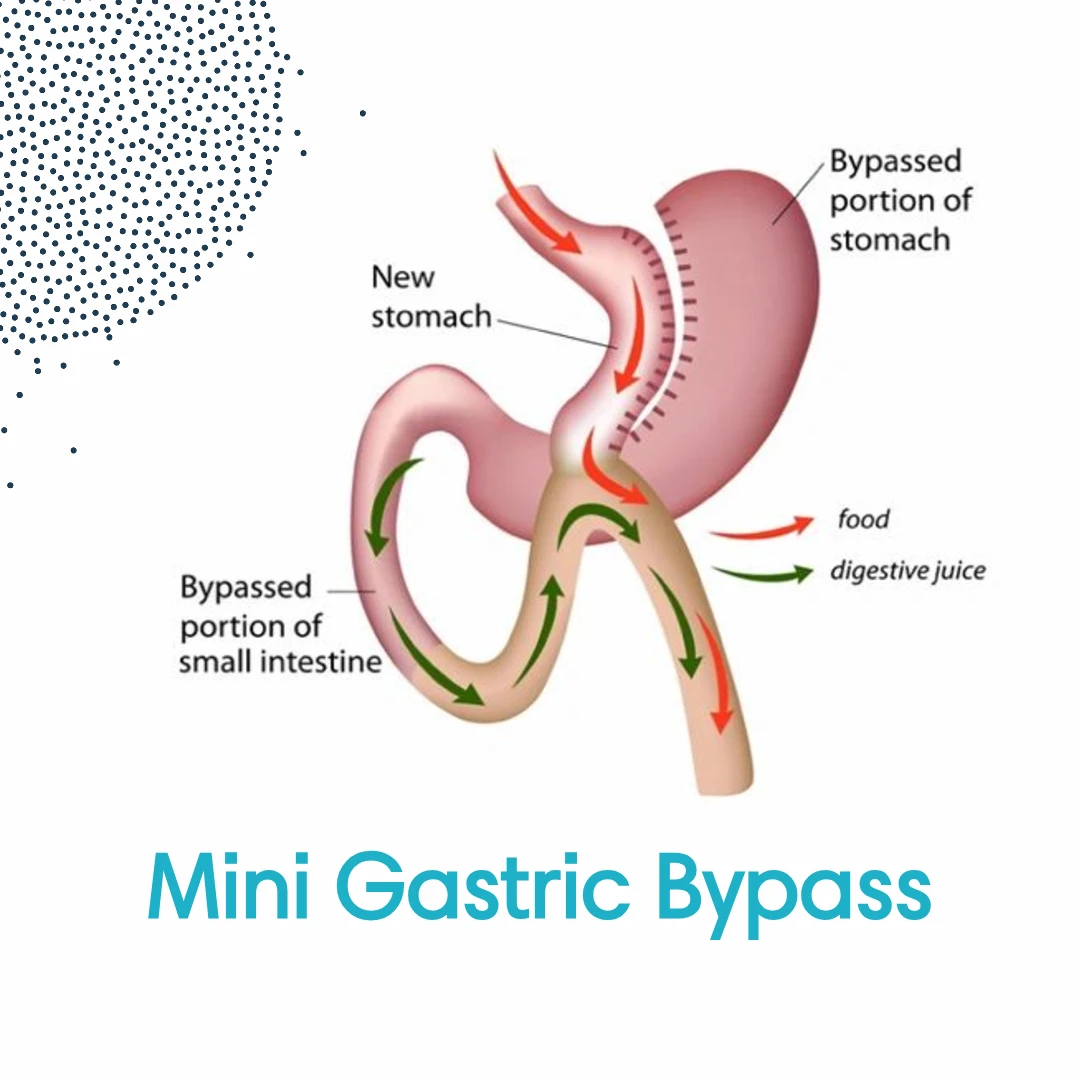
OAGB is a metabolic and weight-loss surgery that involves two main steps:
- Creation of a Small Gastric Pouch: The surgeon divides the stomach to create a small, tube-like gastric pouch that significantly reduces food intake.
- One Anastomosis (Connection): The new gastric pouch is then connected directly to a loop of the small intestine, bypassing the initial section of the small intestine (the duodenum and part of the jejunum). This limits calorie and nutrient absorption.
This single anastomosis design simplifies the procedure compared to the two anastomoses required in RYGB, reducing surgical complexity and operative time.
Benefits of OAGB
OAGB has been recognized for its numerous benefits, making it a favorable option for many patients:
- Effective Weight Loss: Patients typically experience significant and sustained weight loss, with studies showing an average excess weight loss of 60–80% over the first 1–2 years.
- Resolution of Comorbidities: OAGB has proven effective in improving or resolving obesity-related conditions such as type 2 diabetes, hypertension, obstructive sleep apnea, and hyperlipidemia.
- Simplified Surgical Technique: With only one anastomosis, OAGB is technically less complex, which can reduce operative time and lower the risk of complications.
- Reversible Procedure: While intended to be permanent, OAGB is more easily reversible than other bariatric surgeries if necessary.
Potential Risks and Complications
As with any surgical procedure, OAGB is not without risks. Patients should be aware of the following potential complications:
- Bile Reflux: The direct connection of the gastric pouch to the intestine can lead to bile reflux into the stomach, causing discomfort and esophagitis in some patients.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Bypassing a portion of the small intestine reduces nutrient absorption, potentially leading to deficiencies in vitamins and minerals (e.g., iron, calcium, vitamin B12). Lifelong supplementation and regular monitoring are required.
- Dumping Syndrome: Similar to other bypass procedures, patients may experience dumping syndrome, characterized by nausea, diarrhea, and abdominal discomfort after eating certain foods.
- Anastomotic Ulcers: Ulcer formation at the anastomosis site is a known risk and may require medical management.
Eligibility for OAGB
OAGB is generally recommended for patients who:
- Have a BMI of 40 or greater, or a BMI of 35–40 with obesity-related comorbidities.
- Have not achieved sustainable weight loss through diet, exercise, or medical therapy.
- Are committed to lifelong dietary changes, supplementation, and follow-up care.
A thorough evaluation by a bariatric surgeon and a multidisciplinary team is essential to determine eligibility and ensure the procedure is appropriate for the patient’s specific needs.
Postoperative Care and Lifestyle Adjustments
Successful outcomes with OAGB depend on a patient’s adherence to postoperative guidelines, which include:
- Dietary Changes: Patients must follow a gradual diet progression from liquids to solids and adopt healthy eating habits to maintain weight loss.
- Regular Monitoring: Lifelong follow-up appointments with healthcare providers are necessary to monitor nutritional status and overall health.
- Supplementation: Daily intake of vitamins and minerals, including multivitamins, calcium, iron, and vitamin B12, is critical to prevent deficiencies.
Comparing OAGB to Other Bariatric Surgeries
OAGB offers a balance between simplicity and effectiveness. Compared to RYGB, it has a shorter operative time and fewer anastomoses, reducing the risk of leaks and complications. However, the potential for bile reflux is higher in OAGB, making patient selection and monitoring critical. Unlike adjustable gastric banding, OAGB achieves more significant and sustained weight loss but requires more extensive follow-up care.
Conclusion
Simple Gastric Anastomosis Bypass (OAGB) is a highly effective and efficient bariatric surgery option for treating obesity and its related health conditions. Its simplified design, combined with its ability to achieve substantial weight loss and improve comorbidities, makes it an attractive choice for eligible patients. However, the procedure requires lifelong commitment to dietary adjustments, supplementation, and medical follow-up to ensure optimal results and prevent complications.
Patients considering OAGB should consult a qualified bariatric surgeon and a multidisciplinary team to determine the best approach for their individual needs and health goals.